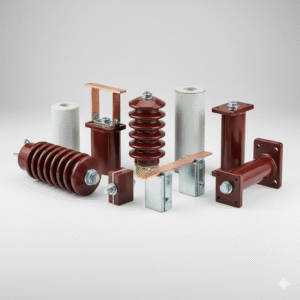
Busbar Insulators
Busbar Insulators are electrical insulating components designed to securely support and isolate busbars in switchgear, distribution panels, and power systems. They prevent unwanted current leakage and electrical faults while providing mechanical stability for high-current busbars. Manufactured from high-strength, heat-resistant materials, busbar insulators ensure safety, durability, and reliable operation in industrial and commercial electrical installations.
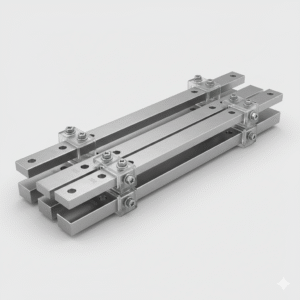
Aluminium Busbar
Aluminium Busbars are lightweight, high-conductivity electrical conductors designed for power distribution and current-carrying applications in electrical systems. Made from high-purity aluminium alloys, these busbars provide excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, reduced weight, and cost efficiency compared to copper. Aluminium Busbars are widely used in switchgear, distribution boards, substations, and industrial power systems for safe and reliable current transfer.
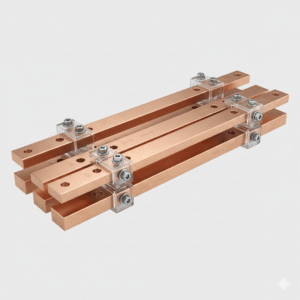
Copper Busbar
Copper Busbars are high-conductivity electrical conductors designed to carry large currents efficiently within switchgear, distribution panels, and power systems. Manufactured from high-purity electrolytic copper, they offer excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, low resistance, and superior mechanical strength. Copper Busbars are widely used in industrial, commercial, and renewable energy applications for safe and reliable current distribution.
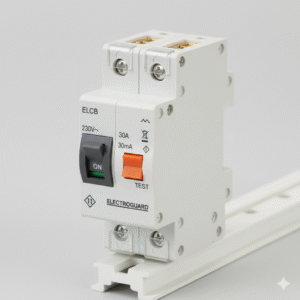
ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker)
ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) is a safety device designed to protect humans and electrical equipment from electric shocks caused by earth leakage currents. It disconnects the power supply when a leakage current is detected, preventing electrocution and reducing fire hazards. ELCBs are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial electrical systems where safety is critical.
RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker)
RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) is a protective device designed to prevent electric shocks and fire hazards by detecting earth leakage currents. It quickly disconnects the circuit when it senses a leakage current, even if there is no overload or short-circuit. RCCBs are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial installations to enhance electrical safety for humans and equipment.
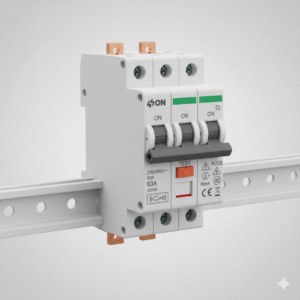
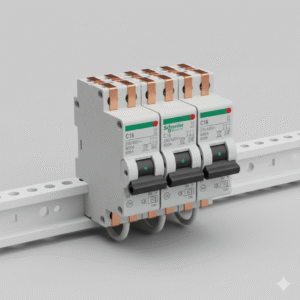
MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)
MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) is a compact electrical protective device used to safeguard electrical circuits against overloads and short circuits. It automatically disconnects power when a fault occurs, preventing damage to wiring, appliances, and electrical systems. MCBs are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications where reliable and quick protection is required for low-voltage circuits.
ACB (Air Circuit Breaker)
ACB (Air Circuit Breaker) is a high-capacity protective device used to protect electrical circuits, transformers, and distribution systems from overcurrent, short circuits, and electrical faults. Unlike MCCBs, ACBs are suitable for higher voltage and current ratings, making them ideal for industrial and commercial power distribution systems. They use air as the arc quenching medium and provide reliable switching, protection, and control for medium-voltage installations.
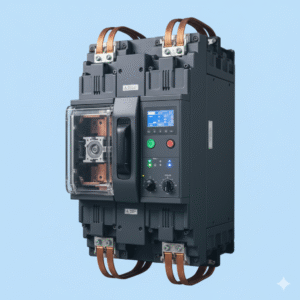
MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker)
MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker) is a robust electrical protective device designed to protect electrical circuits from overcurrent, short circuits, and overload conditions. It combines thermal and magnetic trip mechanisms in a compact, insulated housing to ensure reliable safety and operational continuity. MCCBs are widely used in industrial, commercial, and residential installations where high current ratings and precise protection are required.
High Temperature Cable
High Temperature Cables are specially designed electrical cables capable of operating reliably in extreme heat conditions. Constructed with heat-resistant conductors and insulation materials such as PTFE, Silicone, Fiberglass, or Mica, these cables maintain electrical integrity and mechanical strength at elevated temperatures. They are ideal for industrial furnaces, kilns, ovens, power plants, and other applications where conventional cables cannot withstand high thermal stress.